A Data-Based Perspective on Transfer Learning
Takeaways
-
When doing transfer learning, removing parts of the source dataset may increase the performance on the target dataset.
-
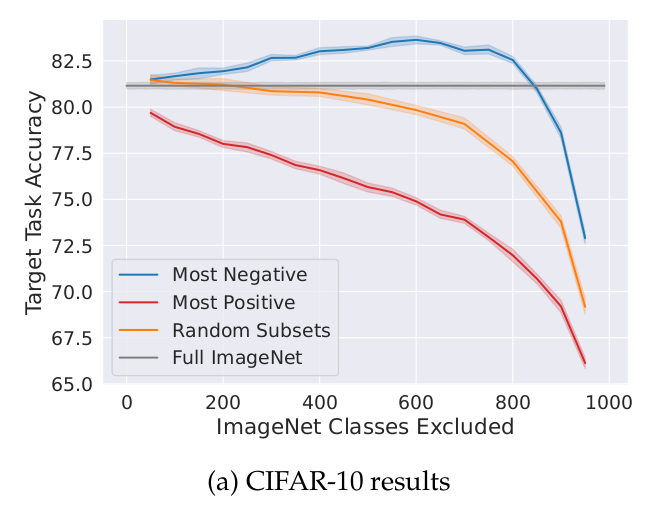
To determine which parts of the source dataset to remove one can train many models on different subsets of the source dataset. In each subset, some classes are removed at random. After evaluating each model on the target dataset, one can estimate the benefit of each source class by calculating the mean accuracy of the models when the class is present minus the mean accuracy when the class is absent. (Note: In this paper, they just studied the classification problem. They also focused on removing whole classes from the source dataset, instead of individual datapoints.)
-
On the ImageNet to CIFAR-10 transfer, the target accuracy improves by 2.5% when removing approximately 600 classes from the source dataset (see image above).
My remarks
- It is an interesting method, but it may be difficult to use in real applications because it requires training the model on the source dataset (which is normally large) many times. For instance, in the paper, they trained 7540 models.